Laboratory Testing
Sample Collection and Preparation:
- Soil and rock samples are collected from boreholes, test pits, or other subsurface exploration methods.
- Representative sampling is crucial to ensure the laboratory test results accurately reflect the in-situ conditions.
- Care is taken to preserve the integrity of the samples during transport to the laboratory.
- Special precautions are employed to prevent changes in moisture content, which can affect test results.
- All lab testing is handed over to our sister company PT. Geoland Quattro Technolab (Rock Mechanics) and PT. Minearth Solution (Soil Mechanics).
Soil Engineering Properties Testing
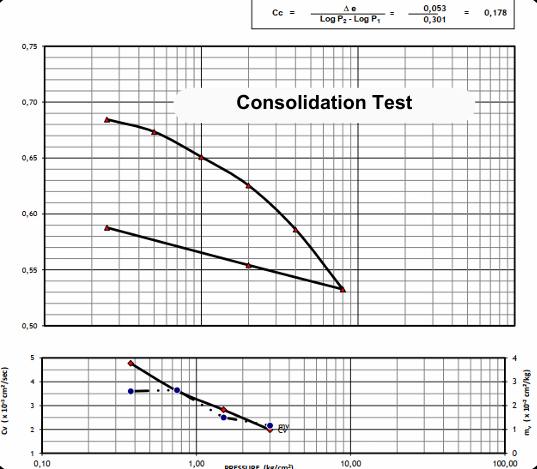
Consolidation Testing:
- Evaluates the compressibility and settlement characteristics of soil under loads.
- Helps estimate settlement and assess the time-dependent behavior of soils.
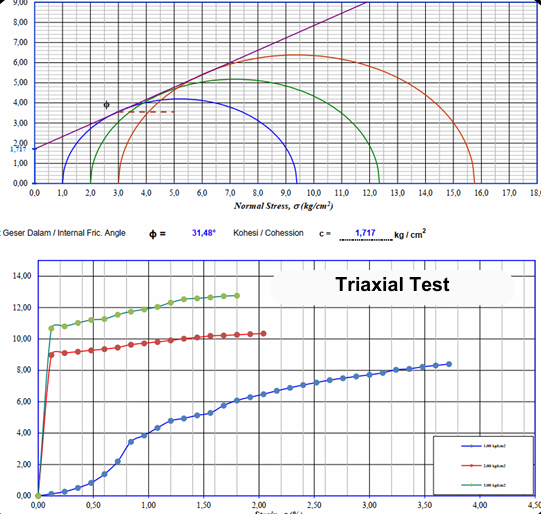
Triaxial Shear Testing:
- Measures the shear strength and stress-strain behavior of soil samples under different confining pressures.
- Essential for slope stability analysis, foundation design, and understanding soil behavior under load.
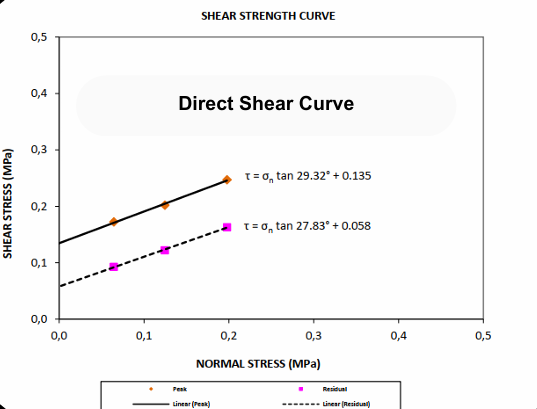
Direct Shear Testing:
- Determines the shear strength of soils by applying a direct horizontal force.
- Commonly used for cohesionless soils and provides valuable input for slope stability studies.
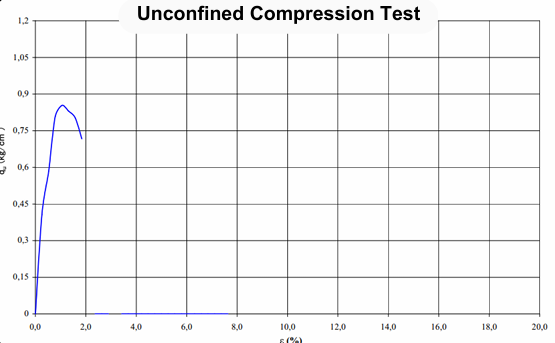
Unconfined Compression Testing:
- Measures the compressive strength of cohesive soils without lateral confinement.
- Useful for characterizing the strength of soft soils.
Rock Mechanics Testing
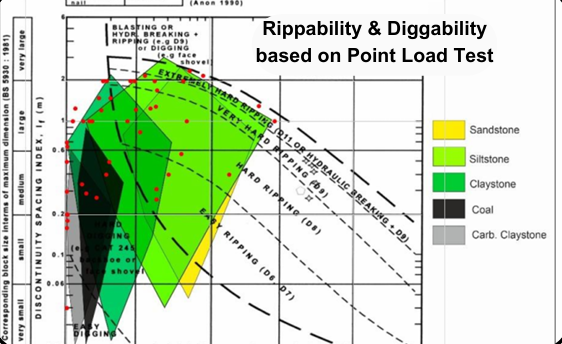
Point Load Index Testing:
- Measures the strength of rock samples under point load conditions.
- Provides a quick assessment of rock strength for preliminary design considerations.
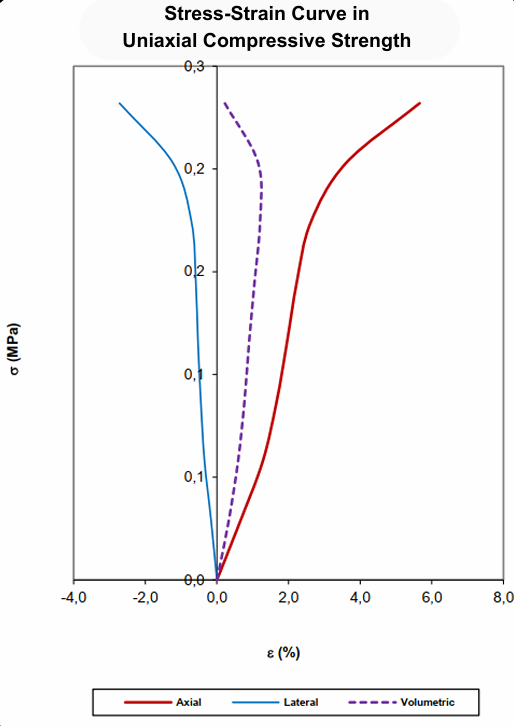
Uniaxial Compression Testing:
- Applies axial load to rock samples to determine compressive strength and modulus of elasticity.
- Critical for understanding the load-bearing capacity of rocks in engineering projects.
Brazilian Test:
- Evaluates tensile strength by inducing a tensile stress across the center of a disc-shaped rock sample.
- Useful for assessing rock durability and fracture behavior.
Permeability Testing:
- Constant Head and Falling Head Permeability Tests.
- Assess the ability of soils to transmit water under different hydraulic gradient conditions.
- Important for groundwater flow analysis, seepage studies, and design of drainage systems.
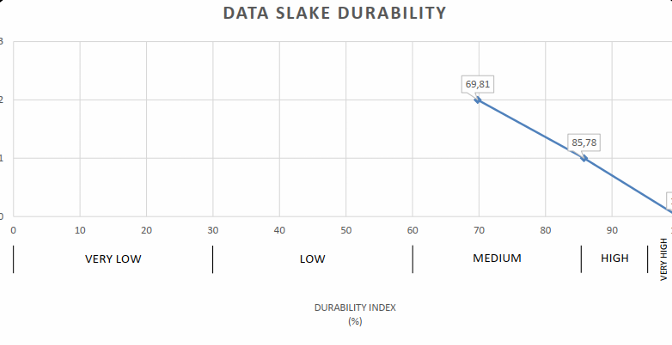
Slake Durability Testing:
- Evaluate the resistance of rock to weathering, especially when subjected to wetting and drying cycles.
- Evaluate the long-term stability of rocks, especially in terms of their ability to withstand the effects of moisture and environmental stressors.