Geological Modelling
3D Geological Modeling:
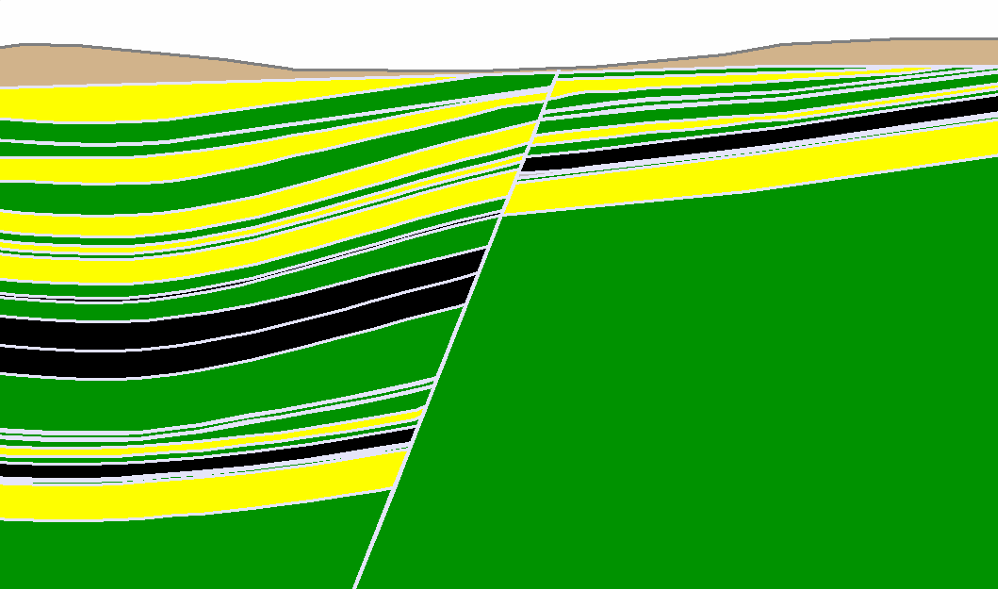
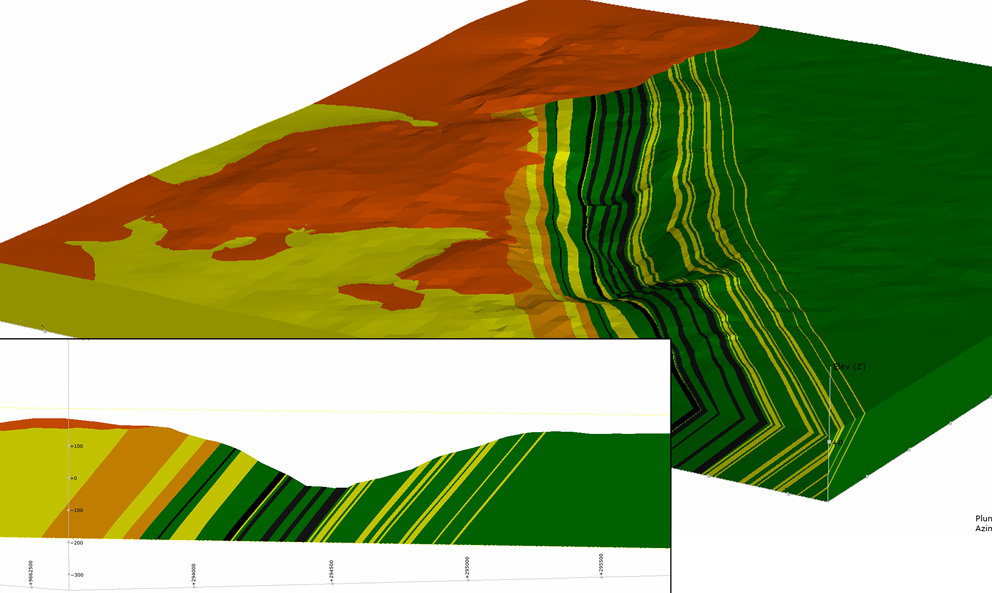
- Utilizes advanced software to create three-dimensional models of subsurface geology, providing a visual representation of geological structures and variations.
- Integrates data from drilling, geophysical surveys, and other sources to enhance understanding of the geological setting.
Integration with Geotechnical Data:
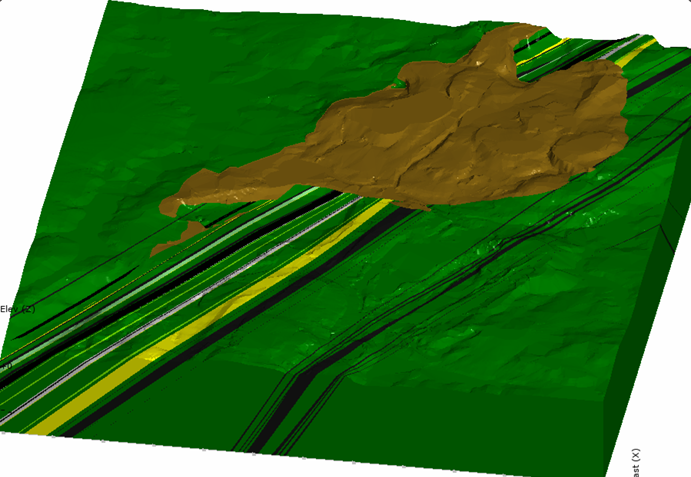
- Incorporates geotechnical data into geological models to better understand the distribution of rock types, fault lines, and other geological features affecting ground stability.
- Enables a seamless transition between geological and geotechnical investigations for a more holistic analysis.
Geological Strength Parameter Mapping:
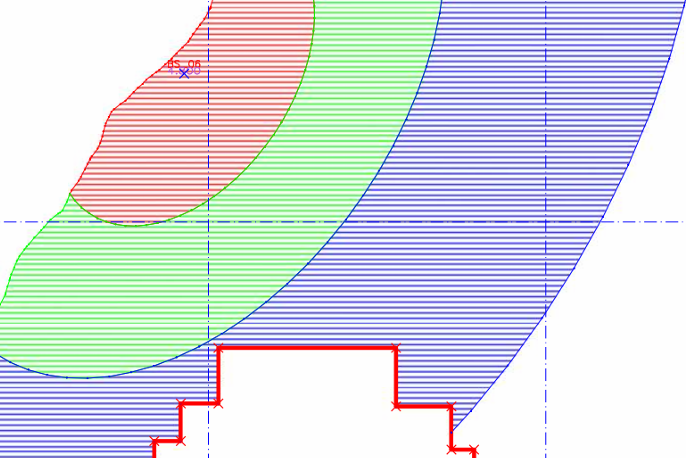
- Maps geological strength parameters, such as rock cohesion and internal friction angles, to assess the geotechnical properties of different geological units.
- Facilitates targeted geotechnical investigations by identifying areas with higher or lower stability potential.
Model Validation:
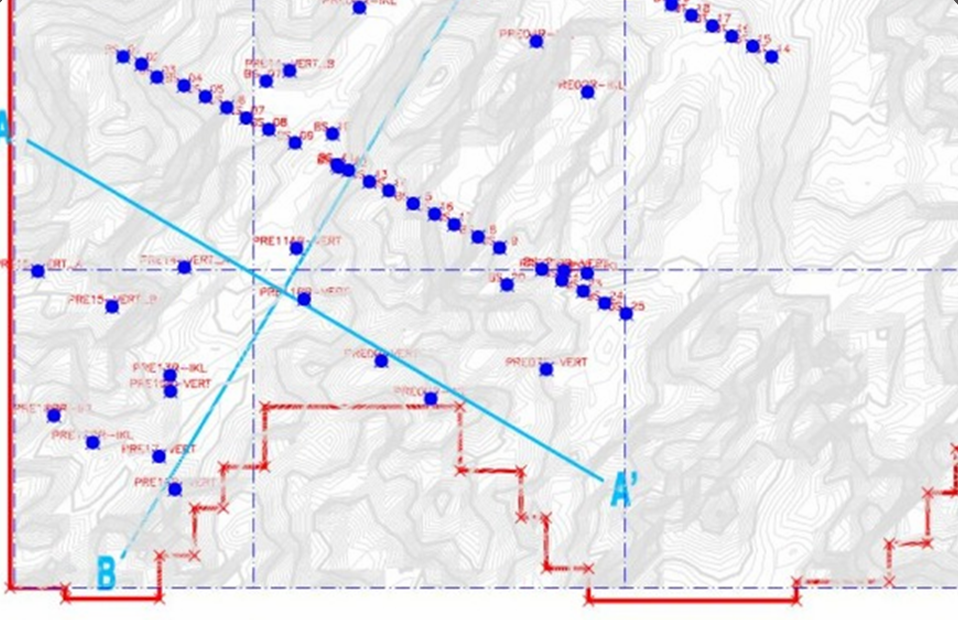
- Validates geological models using field data, drilling results, and geotechnical measurements to ensure accuracy and reliability.
- Adjusts and refines models based on additional data collected during the geotechnical investigation process.